A twisted world — chemists build a molecular banister
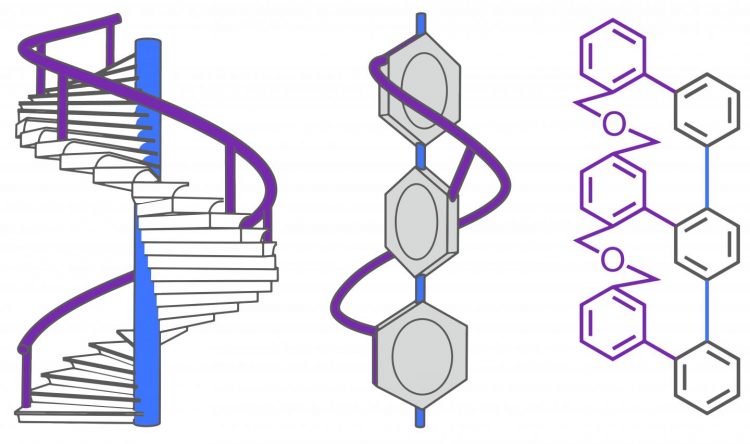
Based on the strands of different lengths (blue and gray), the new helical molecule (right) adopts a spatial arrangement (schematic diagram in the center) that resembles the banister of a spiral staircase (left). Credit: (Fig: University of Basel, Department of Chemistry)
The chemistry of all substances is to a large extent defined by their spatial arrangement. Many molecules can be present in two forms (enantiomers), which behave like a person's right and left hand.
In particular, the organism makes a highly specific distinction between left- and right-handed molecules – a substance can, for example, be extremely active as a drug in one form, while its mirror image is entirely inert. The fundamental understanding of this “chirality”, as it is called, has long been a central component of research in the field of chemistry.
Connecting strands of different sizes
The researchers headed by Professor Marcel Mayor in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel have developed a new approach to contort a small molecule into a form similar in appearance to the banister on a spiral staircase.
At the molecular level, the interlinking of two oligomer strands with different lengths forces to the longer strand to wind around the shorter on its own to balance out the discrepancy in length. This creates a helix with a uniform twisting direction. As a consequence the entire molecule becomes chiral.
The researchers were also able to demonstrate that it is possible to dynamically change the form of the helical molecule from left-handed to right and back again in just a few hours.
“It is not just the structural elegance of this molecule which makes it so unique,” says Mayor. “Above all, it is a completely new way of constructing a continuous helix.”
Efficient procedures for creating chiral compounds generate much interest in basic research and the industrial sector – they can, for example, be used in biological systems research, crop protection chemistry, and the pharmaceutical and fragrance industries. The project was financially supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Original source
Rickhaus, M., Bannwart, L. M., Neuburger, M., Gsellinger, H., Zimmermann, K., Häussinger, D. and Mayor, M.
Inducing Axial Chirality in a “Geländer” Oligomer by Length Mismatch of the Oligomer Strands
Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2014) | doi: 10.1002/anie.201408424
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















