Rapid Detection of Cracks and Corrosion using Magnetic Stray Flux
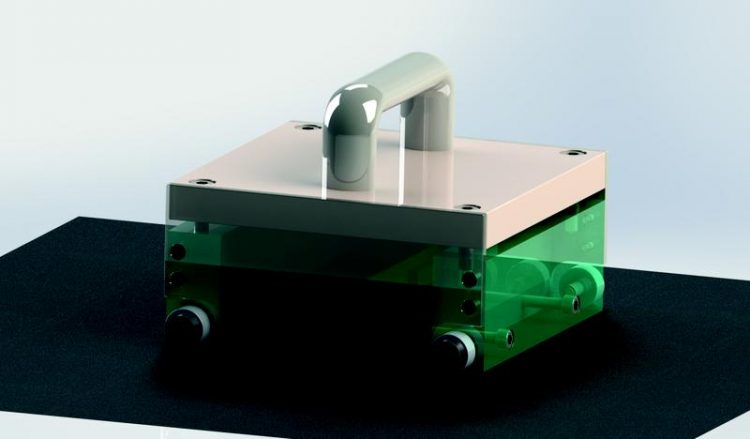
FLUXI: handheld stray flux inspection device (prototype shown) Fraunhofer IZFP
With magnetic stray flux inspections, these flaws can be quickly visualized without destroying or contaminating the material.
As an alternative to magnetic powder tests, this method can also be used wherever the magnetic powder approach is unsuitable.
Engineers at Saarbrucken-based Fraunhofer IZFP will be introducing a mobile handheld device for magnetic stray flux testing at the 29th annual CONTROL trade fair in Stuttgart (hall 1, exhibit booth 1502), which runs May 5 to May 8.
Scientists at the Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP in Saarbrucken have developed a handheld, wireless test device called FLUXI which is based on magnetic stray flux technology.
This method relies on the same physical effect exploited by magnetic powder testing, a standard and widely-used inspection process in steel manufacturing.
When an external magnetic field is applied to sharp-edged cracks on the surface of a component, additional magnetic dipoles form, which then induce magnetic leakage near the surface. This stray field can be detected and processed with magnetic field sensors.
The enormous potential for instrument technology miniaturization provides a key advantage since extremely difficult to access areas of the component can be quickly and easily subjected to magnetic stray flux inspections.
With FLUXI, manufactured parts and components can be rapidly scanned, allowing potential surface defects to be displayed as images.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Innovative Products
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















