Fluid dynamics: Resolving shockwaves more accurately
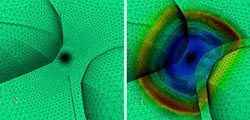
Simulations of shockwaves in fluids as they initiate (left) and propagate (right), using a specially tuned computational mesh. <br>Copyright : 2013 A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing <br>
Vinh-Tan Nguyen and co-workers at the A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing in Singapore have developed a more robust and efficient way to simulate shockwaves under various flow scenarios. Previous techniques for shockwave simulation are specific to particular flow problems, whereas this new method is applicable to shockwaves in any high-speed flow scenario, for example in aerodynamics or explosions.
A shockwave is generated when a discontinuous change in fluid properties follows an abrupt increase in the pressure, temperature and density of the flow. “Strong and unsteady shockwaves can produce oscillations, which affect the stability of numerical solutions in the three-dimensional (3D) computational domain,” explains Nguyen. “The main aim of our technique is to resolve the front of a shockwave while preserving the overall accuracy of the simulation.”
In computational fluid dynamics, flows can be simulated with different levels of accuracy — a low-order approximation is based on a hypothesis, whereas a high-order approximation is one that is closest to reality, or the ‘finest-tuned’ approximation. Simulation accuracy is maintained by using as high-order approximation as possible, as well as by altering the resolution of the 3D computational mesh — a grid of interconnected data points that covers the spatial area of the flow.
“Simulating flows using high-order approximations triggers oscillations, which cause miscalculations at the front of shock waves where the flow is discontinuous,” explains Nguyen. “It therefore becomes counterproductive to have high-order approximations in place right across shock regions.”
To overcome this problem, Nguyen and his team placed a shockwave sensor within the flow to identify high-gradient shockwave fronts as they appeared. They then applied shock capturing schemes to resolve the fronts by reducing the approximation order in those specific regions.
Finally, the researchers increased the spatial resolution of the computational mesh in the localized shock areas to compensate for the lower-order approximations (see image). The 3D mesh is also programmed to rebuild itself following contact with a shockwave.
“With precise detection through the shockwave sensor we can apply the right capturing scheme to treat each shockwave, regardless of its strength,” explains Nguyen. “Our mesh adaptation procedure then simultaneously refines the mesh in shockwave regions and coarsens it in areas of least change, reducing computational costs significantly.”
In addition to its potential application in aerodynamics and blast analysis, the researchers believe that this scheme may be useful for simulating the interface between air and water, with huge potential for marine and offshore applications.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of High Performance Computing
Journal information
Nguyen, V.-T., Nguyen, H. H., Price, M. A. & Tan, J. K. Shock capturing schemes with local mesh adaptation for high speed compressible flows on three dimensional unstructured grids. Computers & Fluids 70, 126–135 (2012).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















