Siemens builds the first European onshore power supply for cruise ships
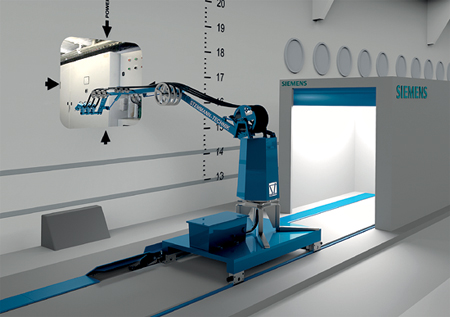
The onshore power supply system from Siemens works with a patented, mobile robot arm designed specifically for the tidal range.
The first European onshore power supply system of this type has a capacity of 12 megavolt amperes (MVA) and works with a patented, mobile robot arm designed specifically for the tidal range. The heart of the system is a frequency converter with control software that adjusts the frequency of the local distribution grid to the ship's electrical system.
The scope of supply for Siemens, in its capacity as general contractor, includes the medium and low voltage switchgears, the transformers, the fire safety system and the building's air conditioning and ventilation system. Commissioning is scheduled for the spring of 2015. The order volume will run to around €8.5 million.
The onshore power supply system from Siemens meets the required international standards IEC/ISO/IEEE 80005-1 (cable connection between shore and ship on the medium voltage side) and IEC 62613-2 (connectors and sockets).
The modular system from Siemens covers all power ranges required in the shipping industry and is suitable for the world's common ship frequencies (50 and 60 Hertz) as well as all necessary voltage levels for shipping. Voltages of 6 or 10 kilovolts (kV) are provided in the 50-Hertz range and 6.6 or 11 kV in the 60-Hertz range. In principle, for example, 50 Hertz AC current is converted to 60 Hertz AC current during frequency conversion.
In the Siemens system, two converters are therefore connected to back to back by a DC link, and each converter is connected to the onshore and onboard converter transformers. As a result, the system is able not only to power an isolated network from a distribution grid but to harmonize power supply grids having different parameters and to connect them to each other.
Siemens uses a multi-level converter on the ship facing side onshore, which guarantees a harmonic-free alternating current characteristic. Converter transformers are used to connect the system to the supply grid. The transformer on the ship facing side ensures galvanic isolation between the ship and shore grids, as required by IEC 80005-1.
The system has a specially developed cable management system for cruise ships that provides a fast, easy and flexible connection between the shore and the ship. The system is self-propelled and can be automatically operated from the ship as needed, so that no additional specialists are needed on shore. A concrete channel along the quay wall guides a high tide-resistant cable chain for system mobility and is designed with a length of 300 meters for this project.
A robot arm is used to transport the power cable connectors and the communication link into the ship through the outer hatch, like on a tray. Developed jointly between Siemens and Stemmann Technik in Schüttorf, this technology also compensates for the tidal range during power supply. Power is transferred to the ship without slip rings, making it immune to dysfunction.
The concrete channel's steel plate cover can easily support the required axle loads, so that telescoping cranes, trucks and buses can drive over the quay operating area with no restrictions during the lay days. The cable management system is stored in a high tide-protected garage when not in operation, thus meeting the Hanseatic City of Hamburg's requirement for granting visitors public access to wharfage.
One of the main causes of local air pollution in ports is the combustion of ship fuels for generating electricity during lay days. Reducing harmful emissions due to shipping is a concern in port cities around the world. For more than ten years now, the European Commission has recommended, through regulations, incentives and access facilitation, that port authorities provide ways for ships to use onshore power sources during lay days in port.
This recommendation was last specified and expanded in 2006. In 2013, the European Commission also drew up a proposal for a directive on “Deployment of alternative fuels infrastructure.” According to this proposal, the greenhouse gas emissions caused by traffic must be lowered by 60 percent by 2050. Alternatives such as electricity at berths and liquefied natural gas (LNG) during transport are gaining in importance in seaports. According to Article 4 of the proposal, the member states are to ensure that an onshore power supply for ships is provided in most seaports and inland harbors.
For further information on onshore power supply, please see www.siemens.com/siharbor
The Siemens Infrastructure & Cities Sector (Munich, Germany), with approximately 90,000 employees, focuses on sustainable and intelligent infrastructure technologies. Its offering includes products, systems and solutions for intelligent traffic management, rail-bound transportation, smart grids, power distribution, energy efficient buildings, and safety and security. The Sector comprises the divisions Building Technologies, Low and Medium Voltage, Mobility and Logistics, Rail Systems and Smart Grid.
For more information visit
http://www.siemens.com/infrastructure-cities
The Siemens Low and Medium Voltage Division (Erlangen, Germany) serves the entire product, system, and solutions business for reliable power distribution and supply at the low- and medium-voltage levels. The Division's portfolio includes switchgear and busbar trunking systems, power supply solutions, distribution boards, protection, switching, measuring and monitoring devices as well as energy storage systems for the integration of renewable energy into the grid. The systems are supplemented by communications-enabled software tools that can link power distribution systems to building or industry automation systems. Low and Medium Voltage ensures the efficient supply of power for power grids, infrastructure, buildings, and industry. Additional information is available on the Internet at: http://www.siemens.com/low-medium-voltage
Reference Number: ICLMV20140503e
Contact
Mr. Heiko Jahr
Low and Medium Voltage Division
Siemens AG
Freyeslebenstr. 1
91058 Erlangen
Germany
Tel: +49 (9131) 7-29575
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















