A small connection with big implications: Wiring up carbon-based electronics
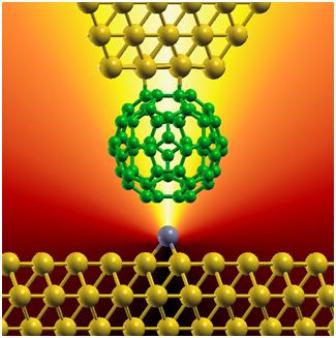
Artistic view of an electric connection between a carbon-based "football" molecule and a single metallic atom (gray ball). The researchers were able to quantify how the current depends on the chemical nature of the contacting atom.
Carbon-based nanostructures such as nanotubes, graphene sheets, and nanoribbons are unique building blocks showing versatile nanomechanical and nanoelectronic properties. These materials which are ordered in the nanoscale, that is, in the dimension of a millionth of millimetre, are promising candidates to envision applications in nanoscale devices, ranging from energy conversion to nano-electronic transistors.
A good connection between carbon-based materials and external metallic leads is of major importance in nanodevice performance, an aspect where an important step has been surmounted by researchers from UPV/EHU, DIPC and CNRS by studying contacts of carbon nanostructures with atoms of different chemical nature.
The chemical nature of contacting leads is of major importance as it affects the electronic properties and the geometry of the contact. The impact of these two aspects on the transport properties are entangled and this group studied these two parameters for contacts shrunk to the limit of individual atoms as for large structures it is challenging to address them separately.
In close collaboration, the researchers used a prototype carbon-based molecule made of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a sphere that can be viewed as a graphene sheet rolled into a tiny ball. The experimental team in Strasbourg led by Guillaume Schull, attached this molecule to the apex of an extremely tiny metal needle of a scanning tunnelling microscope.
The molecule-terminated needle was then cautiously approached to individual metallic atoms of different chemical nature up to the formation of a robust connection. By simultaneously measuring the electrical current passing through these connections, they could deduce which of the individual metallic atom is injecting charges to the carbon-made molecule with the greatest efficiency.
Large-scale computer simulations performed by the theoretical team in San Sebastian led by Thomas Frederiksen, Ikerbasque Research Professor at the DIPC, revealed a fascinating and unexpected aspect of these extremely tiny connections: their electric and mechanical properties are in fact representative for much larger carbon-based materials.
These results, published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, set the bases to find extremely efficient contacts in the near future. The study paves the way to probe a great number of different metallic species (as well as tiny alloys made of two or three different metallic atoms), allowing for a systematic classification of their abilities to inject electrons into emerging carbon-based electronic devices.
Full research publication (open access)
Chemical control of electrical contact to sp2 carbon atoms
T. Frederiksen, G. Foti, F. Scheurer, V. Speisser, & G. Schul. Nature Communications (2014).
DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4659
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…