Tropical Storm Roke Closing in on Kadena Air Base: Infrared NASA Satellite Imagery
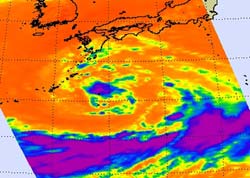
This infrared image of Tropical Storm Roke was captured on Sept. 14 at 10:41 p.m. EDT. The purple area around the center of circulation indicates the coldest, highest cloud heights, where the heaviest rain was occurring. The orange indicates warm sea surface temperatures over 80F that are allowing Roke to intensify. Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen <br>
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Roke yesterday and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed powerful convection building around the storm's center and over the northern edge. Meanwhile, dry air is wrapping into the low-level center from the southwest, and limiting cloud development.
Infrared imagery provides forecasters with an inside look into the cloud temperatures and heights, and the colder and higher the clouds go, the stronger they become. Meteorologists at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center use infrared imagery to help create their forecasts. AIRS data also showed sea surface temperatures around Roke to be near 27 degrees Celsius (81 Fahrenheit).
On Sept. 15 at 11 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm Roke was located approximately 175 nautical miles east of Kadena Air Base, Japan, and is moving west at 6 knots (7 mph). Roke is a minimal tropical storm with maximum sustained winds near 35 mph, but expected to strengthen as it closes in on Kadena Air Base. Warm water temperatures (over 80F/26.6C) and low wind shear are allowing Roke to intensify. Tropical storm conditions are expected at the base from Friday, Sept. 16 through Sunday, Sept. 18 as Roke continues on its westward track.
Text credit: Rob Gutro,
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















