Stunning NASA infrared imagery of Hurricane Igor reveals a 170 degree temperature difference
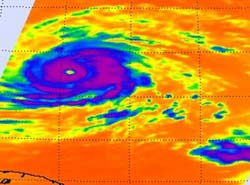
This impressive infrared image of Hurricane Igor from NASA\'s AIRS instrument shows a clear and large eye, and very strong convection (purple) and high, powerful thunderstorm cloud tops around his center. The image was captured from the AIRS instrument on NASA\'s Aqua satellite on Sept. 14 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT). Note the warm ocean temperatures (dark orange) well over the 80 degree F threshold needed to maintain intensity.<br><br>Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Igor on Sept. 14 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured icy cold cloud top temperatures in the strong thunderstorms that surround Igor's well-defined eye. Those cloud top temperatures were as cold or colder than -90F, indicating they were near the top of the troposphere, and very strong.
The infrared imagery also showed the warmer, open 20 nautical-mile wide eye (because it was not cloud-filled). In addition, AIRS got a reading on the sea surface temperatures around Igor, which were all warmer than the 80F threshold needed to maintain a tropical cyclone, so Igor has a good energy source for the next day or two. So, the difference between Igor's cold cloud top temperatures and the warm ocean surface waters that are powering it are greater than 170 degrees Fahrenheit!
The AIRS instrument is managed out of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. and NASA's Ed Olsen creates those stunning images.
At 11 a.m. EDT today, Sept. 14, Hurricane Igor was still a category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale with maximum sustained winds near 135 mph. It was located far from land, about 710 miles east of the Northern Leeward Islands, near 18.3 North and 52.3 West. It was moving west-northwest near 7 mph, and is forecast by NOAA's National Hurricane Center to turn toward the northwest on Wednesday. Igor's minimum central pressure is 945 millibars.
Although Igor is over 700 miles from the Northern Leeward Islands, large ocean swells will reach them today creating dangerous conditions at beaches. Large swells will reach Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands later today and tomorrow. These dangerous surf conditions also create rip currents along the beaches.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















