NASA View of Atlantic's Tropical Depression 19 Shows Backwards "C" of Strong Storms
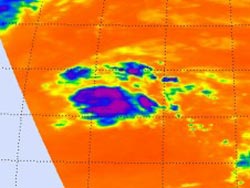
Infrared satellite imagery on Oct. 22 at 12:23 p.m. EDT, from the AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite showed that the strongest thunderstorms in Tropical Depression 19 stretched from the northeast to the southeast of the center of the depression's circulation. Those thunderstorms are reaching high into the troposphere where cloud top temperatures are as cold (purple) as -63F. <br>Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen <br>
Infrared satellite imagery taken on Oct. 22 at 12:23 p.m. EDT, from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed that the strongest thunderstorms in Tropical Depression 19 stretched from the northeast to the southeast of the center of the depression's circulation.
Those thunderstorms are reaching high into the troposphere where cloud top temperatures are as cold (purple) as -63F. The AIRS image was created at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
On Oct. 23, infrared satellite imagery revealed the same story about Tropical Depression 19's (TD 19) structure. The National Hurricane Center noted “The structure of the depression consists of a small but persistent cluster of deep convection regenerating near the center of circulation and an outer band farther to the north and northeast.”
On Oct 23 at 11 a.m. EDT, TD19's maximum sustained winds were near 35 mph (55 kph). Some strengthening is possible over the next couple of days, and the depression could become a tropical storm.
The center was located near latitude 25.7 north and longitude 51.0 west, about 915 miles (1,470 km) northeast of the Leeward Islands. TD19 is moving to the north-northeast near 15 mph (24 kph) and is expected to move northeastward to east-northeastward on Oct. 24. TD19 formed in the central Atlantic yesterday, Oct. 22. If TD19 gets named, it would be dubbed “Tony.”
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















