NASA Sees Tropical Cyclone Colin Coming "Unwound"
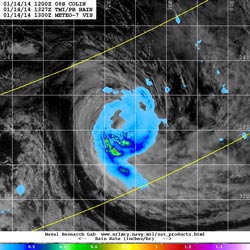
The TRMM satellite flew over Colin on January 14 at 1327 UTC/8:27 a.m. EST and found that light rain surrounded the tropical cyclone with the exception of moderate to heavy rain in the southern quadrant. <br>Image Credit: NRL/NASA/ESA<br>
On January 14, 2014 at 0900 UTC, Colin had maximum sustained winds near 40 knots/46.0 mph/74.0 kph. It was far from land, and centered 1,171 nautical miles/1,348 miles/2,169 km from Diego Garcia near 26.7 south and 73.3 east. Colin was moving to the south at 9 knots/10.3 mph/16.67 kph.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Colin at 0840 UTC/3:40 a.m. EST on January 14 and obtained a visible look at the clouds and structure of the storm. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer known and MODIS captured the image that showed thinning clouds in all quadrants except the southern quadrant where TRMM confirmed the heaviest rainfall was occurring almost five hours later when it passed overhead.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's TRMM satellite or Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission, flew over Colin on January 14 at 1327 UTC/8:27 a.m. EST and measured rainfall in the storm. TRMM found that light rain surrounded the tropical cyclone with the exception of moderate to heavy rain in the southern quadrant.
According to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, animated multispectral satellite imagery showed that the low-level center of circulation was exposed and after the TRMM overpass, convection has waned more, leaving almost no strong convection in the tropical cyclone. Satellite data showed that the overall low-level structure was becoming less tightly wrapped.
Colin continues to head into cooler sea surface temperatures which will continue to weaken the storm as it is expected to become a cold-core low pressure area. Vertical wind shear is also increasing, so Colin's end is likely in the next couple of days.
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















