NASA Sees Heavy Rains and Hot Towers in Hurricane Manuel
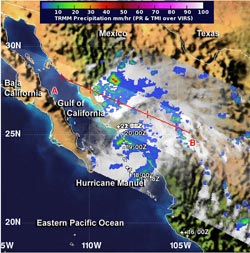
NASA's TRMM satellite flew over Tropical Storm Manuel at 9:16 p.m. EDT on Sept. 18, and it observed areas of heavy rainfall (red)around the storm's center and in a band of thunderstorms north of the center. TRMM also observed hot towers, or towering thunderstorms that were over 16 km/9.9 miles high.<br><br>Image Credit: NASA/SSAI, Hal Pierce<br>
TRMM noticed heavy rainfall and some hot towering thunderstorms, which were indications that the storm was intensifying. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image that showed Manuel was making landfall during the morning of Sept. 19, and at 11 a.m. EDT, Hurricane Manuel officially made landfall near Culican, Mexico.
A Hurricane Warning is in effect for La Cruz to Topolobampo and a Tropical Storm Watch is in effect from north of Topolobampo to Huatabampito.
When NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM flew over Tropical Storm Manuel on Sept. 19 at 0116 UTC/9:16 p.m. EDT on Sept. 18, it observed areas of heavy rainfall around the storm's center and in a band of thunderstorms north of the center. TRMM also observed hot towers, or towering thunderstorms that were over 16 km/9.9 miles high.
A “hot tower” is a tall cumulonimbus cloud that reaches at least to the top of the troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere. It extends approximately 9 miles/14.5 km high in the tropics. The hot towers in Manuel were over 9.9 miles/16 km high. These towers are called “hot” because they rise to such altitude due to the large amount of latent heat. Water vapor releases this latent heat as it condenses into liquid. NASA research shows that a tropical cyclone with a hot tower in its eyewall was twice as likely to intensify within six or more hours, than a cyclone that lacked a hot tower. When TRMM passed over Manuel and captured the hot towers, it was just about one hour after the National Hurricane Center classified the storm as a hurricane.
The heavy rain observed by TRMM was an indication of the rainfall that Manuel is expected to bring to northwestern Mexico. According to the National Hurricane Center (NHC), Manuel is expected to produce 8 to 12 inches of rain over the Mexican state of Sinaloa with isolated maximum amounts of 20 inches possible. An additional 1 to 2 inches of rain is also possible over the southern portion of the Baja California peninsula and the state of Nayarit.
Storm surge with water levels as much as 2 to 4 feet above normal tide levels are possible along the coast near and to the south of where the center makes landfall, NHC noted. The surge will be accompanied by large and destructive waves. NHC noted that tropical storm conditions are possible in the northern portion of Sinaloa and extreme southern Sonora within the tropical storm watch area.
On Sept. 19 at 5:11 a.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Hurricane Manuel's very cold cloud tops and powerful thunderstorms as it was making landfall. Some cloud top temperatures exceeded -63F/-52C indicating they were high in the troposphere and had the potential to drop heavy rainfall.
At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 19, Manuel's maximum sustained winds were near 75 mph/120 kph when its center came ashore in Culiacan, Mexico. It was near 25.0 north and 107.8 west. Manuel is moving north near 3 mph/ 6 kph and is expected to turn to the north-northeast is expected later today. The NHC expects Manuel to weaken to a tropical depression late tonight or early Friday, Sept. 20, finally dissipating over the mountains of Mexico late on Sept. 20.
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…





















