NASA Sees Development of Tropical Storm 09S in Southern Indian Ocean
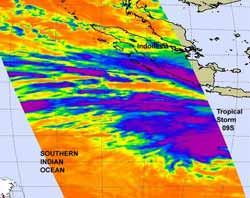
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 09S on January 25 at 7:05 UTC (2:05 a.m. EST) the AIRS instrument measured the temperatures of the low pressure area's cloud tops. Thunderstorm cloud tops around the entire center of circulation and in some of the bands of thunderstorms that circled the center from northwest to northeast were colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52.7 Celsius). Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen <br>
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 09S on January 25 at 7:05 UTC (2:05 a.m. EST), and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument measured the cloud top temperatures.
Just as they appeared in infrared imagery on January 24, thunderstorm cloud tops around the entire center of circulation and in some of the bands of thunderstorms that circled the center from northwest to northeast were colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52.7 Celsius).
Temperatures that cold indicate uplift (and evaporation) of air is very strong, and it pushes the cloud tops to the top of the troposphere. When cloud tops get that high, they tend to drop heavy rainfall (around 2 inches/50 mm per hour).
AIRS infrared imagery revealed that the convection continues to strengthen and during the early hours on January 25, bands of thunderstorms were developing around the center.
Although Tropical Storm 09S has moved in a westerly direction over the last couple of days, a weather system (elongated area of high pressure, called a ridge) will begin pushing it eastward toward Western Australia late on January 25. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center has forecast Tropical Storm 09S (TS09S) to come closest to the coastline of Western Australia by January 29 and 30, 2012.
At 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST) on January 25, TS09S had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/~65 kph). It was located near 16.0 South latitude and 107.8 East longitude, about 515 nautical miles (~592 miles/~953 km) northwest of Learmonth, Australia. The storm was still moving to the west at 5 knots (~6 mph/9 kph), but is expected to change course to the east-southeast.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects that Tropical Storm 09S will continue to strengthen over the next couple of days and could reach Cyclone status.
Text Credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…




















