NASA satellites see Tropical Storm Matthew grow quickly, warnings up in Central America
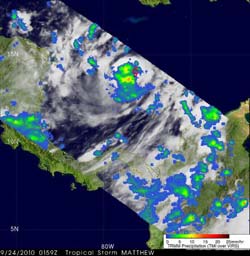
TRMM data from Sept. 24 at 0159 UTC showed moderate to heavy rainfall (red) southwest of Matthew\'s center of circulation. The approximate center of circulation is shown by a red tropical storm symbol. Credit: NASA/SSAI, Hal Pierce<br>
Cloud top temperatures indicate the strength of the storm to forecasters. The colder the cloud top temperatures, the stronger the convection and uplift. When cloud top temperatures drop, as they did in Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) imagery captured on Sept. 23 at18:53 UTC (2:53 p.m. EDT) it indicates the storm is gaining strength.
At that time, Matthew's maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph. In the image, the coldest cloud top temperatures (colder than -63 Fahrenheit) appeared around the center of Matthew's circulation already giving the appearance of an eye. The AIRS infrared image on Sept. 24 at 3:05 a.m. EDT showed a concentrated area of strong thunderstorms around Matthew's center as the sustained winds had increased to 50 mph.
AIRS has the ability to determine cloud top and sea surface temperatures from its position in space aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. Cloud top temperatures help forecasters know if a storm is powering up or powering down and Matthew is powering up.
In addition to the Aqua satellite, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew nearly above Matthews's location on Sep. 24 at 0159 UTC (9:59 p.m. EDT Sept. 23) capturing data used in a rainfall analysis done at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) data analyzed from this orbit showed moderate to heavy rainfall southwest of MATTHEW's center of circulation.
At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 24, Matthew's maximum sustained winds were near 50 mph, and strengthening is expected in the warm Caribbean waters, so the National Hurricane Center said that Matthew could become a hurricane by Saturday. Meanwhile at 11 a.m. Sept. 24, Matthew was located about 80 miles east of Cabo Gracias a Dios, Nicaragua, near 14.4 North and 82.2 West. It was moving west at 20 mph, and had a minimum central pressure of 1001 millibars. Just 15 hours before, its minimum central pressure was 1005 millibars, and a drop in pressure indicates a strengthening storm.
A hurricane watch is in effect for Puerto Cabezas, Nicaragua to Limon, Honduras including the offshore islands. A tropical storm warning is in effect for Puerto Cabezas, Nicaragua to Limon, Honduras including the offshore islands.
A tropical storm warning is in effect for Puerto Cabezas, Nicaragua northward to the border with Honduras including the offshore islands and the coast of Honduras including the offshore islands. A tropical storm watch is in effect for the coast of Belize, while a hurricane watch is in effect for Puerto Cabezas, Nicaragua to Limon, Honduras. Hurricane conditions are possible between 11 p.m. EDT tonight and 11 a.m. EDT Saturday in that watch area.
Tropical storm-force winds are expected to reach the coastal warning areas during the afternoon of Sept. 24, and a storm surge is expected to produce flooding and dangerous surf. Expected rainfall amounts of 6 to 10 inches are forecast with isolated amounts to 15 inches.
According to the National Hurricane Center in Miami, on the forecast track the center of the Matthew is expected to be near the Nicaragua/Honduras border late Friday or early Saturday morning then move over land in northern Honduras on Saturday. Updates on Matthew can be found at the National Hurricane Center's web page: www.nhc.noaa.gov.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















