NASA satellites see Nicole become a remnant, another low soaking US East Coast
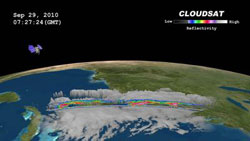
NASA\'s CloudSat satellite passed through the western section of Tropical Storm Nicole on Sept. 29, 2010, at 0727 UTC (3:27 a.m. EDT). The CloudSat image captured areas of light cumulus precipitation mixed with a stream of mid- level cloudiness, most likely altocumulus and altostratus. Deep mid-level flow from the south-southwest was evident in the image, occurring from the inclination of the clouds towards the north-northeast. Credit: NASA/JPL/Colorado State Univ./NRL<br>
While Nicole weakened, a huge trough of low pressure over the U.S. eastern seaboard from Florida to Maine has become the key weathermaker there. The trough, an elongated area of low pressure, is streaming tropical moisture from Nicole's remnants and the Gulf of Mexico, bringing high rainfall totals and severe weather up and down the coast.
At 2 a.m. EDT on Sept. 30, Nicole's remnant low was still 35 miles east of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. and about 65 miles west-southwest of Freeport, the Bahamas. Nicole's remnants are forecast to merge with the giant trough (an elongated area of low pressure) later today or early Friday. Nicole's remnants, barely discernable on satellite imagery now because of the huge trough to its west, will still be bringing locally heavy rainfall over the Bahamas. There's just a 10 percent chance it will regenerate as a subtropical cyclone in the next 24 hours.
The GOES-13 satellite captured a visible image of the extensive cloud cover of the trough (elongated area of low pressure) all along the U.S. East coast on Sept. 30 at 1345 UTC (9:45 a.m. EDT) that is feeding off tropical moisture from the Gulf of Mexico, and Nicole's remnants. GOES satellites are operated by NOAA and the NASA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. uses the satellite data to create images and animations.
NASA's CloudSat satellite passed through the western section of Tropical Storm Nicole on September 29, 2010 at 0727 UTC (3:27 a.m. EDT). CloudSat captured an image of the elongated storm system when it was located between Cuba and Florida was in the beginning stages of tropical cyclone formation. CloudSat imagery noticed that low level cyclonic circulation was developing around the low pressure area, as it was being fueled by warm sea surface temperatures.
The CloudSat image captured areas of light cumulus precipitation mixed with a stream of mid- level cloudiness, most likely altocumulus and altostratus. Deep mid-level flow from the south-southwest was evident in the image, occurring from the inclination of the clouds towards the north-northeast.
On Sept. 28 at 18:20 UTC 2:20 p.m. EDT the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Nicole over Cuba before it weakened back into a tropical depression. Nicole was already losing her cyclonic shape at that time.
The National Hurricane Center issued its final official forecast for Nicole on Sept. 29 at 5 p.m. EDT. At that time, Nicole had maximum sustained winds near 40 mph. It was about 175 miles east-northeast of Havana, Cuba and 165 miles west of Nassau near 24.5 North and 80.0 West. It was moving north-northeast near 12 mph and had a minimum central pressure of 996 millibars. At that time, it had degenerated into an elongated area of low pressure and the National Hurricane Center noted that the ill-defined low had become untrackable.
Forecasters are also watching a low pressure area in the eastern Caribbean. A large area of disturbed weather associated with two tropical waves is about 800 miles east of the Windward Islands. The showers and thunderstorms in it are currently disorganized but it is expected to move into more favorable conditions. It currently has a 30 percent chance of becoming a tropical depression in the next 48 hours, so Cuba is watching it closely after being soaked by Nicole.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















