NASA Satellite sees most of Cyclone Bingiza's rainfall over Mozambique Channel
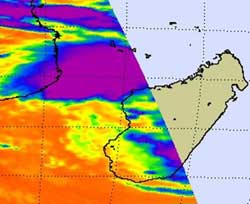
NASA\'s Aqua satellite captured cold thunderstorm cloud tops (purple) to the north and west of the center of Tropical Storm Bingiza in this infrared image of Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC. Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Madagascar this morning, Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC (6:11 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument read the temperatures of the cold thunderstorm cloud tops in Cyclone Bingiza. Most of the strongest thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation already over the Mozambique Channel, while Bingiza's center remains over the western part of the island nation.
At 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST) on Feb. 15, Tropical Cyclone Bingiza had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/64 kmh) so it was still a tropical storm. It was centered about 180 miles (289 km) north-northwest of Antananarivo, Madagascar, near 16.4 South and 45.2 East. It was moving west near 10 knots (11 mph/18 kmh).
At 1 a.m. EST (0600 UTC) Majunga, Madagascar reported north winds at 17 knots (20 mph/31 kmh) and an atmospheric pressure of 997 millibars. Majunga is a seaport city, a district, and a province on the northwest coast of Madagascar. Mahajanga is the capital city of the Boeny region as well as the Mahajanga Province.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Bingiza to move entirely into the eastern Mozambique Channel later today. A trough (elongated area) of low pressure will then push Bingiza parallel to the western coastline of Madagascar and forecasters expect the warm waters of the Channel and the low wind shear to allow it to re-strengthen. Bingiza is expected to turn toward the east and make a second landfall in southwestern Madagascar later this week.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















