NASA catches Tropical Cyclone Amara's stretched out eye
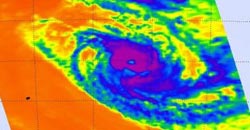
NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of Tropical Cyclone Amara in the South Indian Ocean on Dec. 18 at 09:05 UTC/4:05 a.m. EST and showed powerful thunderstorms (purple) around the storm's eye.<br><br>Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team<br>
Tropical Cyclone Amara is spinning in the Southern Indian Ocean along with Tropical Cyclone Bruce, and both share elongated shapes. Even Amara's 10 nautical-mile-wide eye appeared stretched out.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible picture of the storm on December 18 at 09:05 UTC/4:05 a.m. EST that showed that the eye was also cloud-filled. The MODIS image also showed bands of thunderstorms were wrapping into the center of circulation from the northeast and southwest.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST on December 18, Amara's maximum sustained winds had increased to 80 knots/92.0 mph/148.2 kph. Amara was centered near 16.0 south latitude and 70.5 east longitude, about 543 nautical miles/624.9 miles/1,006 km south of Diego Garcia. Amara has tracked to the west at 3 knots/3.4 mph/5.5 kph.
Amara is in an environment of low wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures that will allow it to continue to intensify, even rapidly. Amara is moving between two subtropical ridges (elongated areas) of high pressure. In three days Amara is forecast to encounter increasing wind shear which will weaken the system. High pressure is also expected to build south of Amara, which should slow it down and bring in cooler, drier air, which will also weaken the tropical cyclone.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















