NASA's Aqua satellite shows strongest side of Tropical Storm 13W
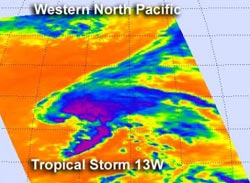
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on Aug. 6 at 0205 UTC (Aug. 5 10:05 a.m. EDT). The AIRS instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms (purple) and heaviest rainfall north and east of the center of circulation.<br><br>Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on August 6 at 0205 UTC (Aug. 5 10:05 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms (purple) and heaviest rainfall north and east of the center of circulation.
Infrared imagery shows temperature and the higher the cloud tops, the colder they are as they reach higher in the troposphere (lowest atmospheric layer). When cloud top temperatures are very cold, it's an indication of strong uplift in the atmosphere. The cloud top temperatures north and east of Tropical Storm 13W's center of this low were near -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius), and indicated powerful uplift and high cloud tops.
At 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) on August 6, Tropical Storm 13W had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kmh). It was located about 550 nautical miles (632 miles/1019 km) north-northwest of Wake Island near 28.2 North and 162.5 East. It was moving to the north-northwest at 13 knots (15 mph/24 kmh).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect that the tropical storm should maintain intensity while staying at sea over the next several days. Vertical wind shear is expected to decrease and sea surface temperatures are near 26.6 Celsius (80 Fahrenheit), which is needed to maintain a tropical cyclone. The tropical storm is expected to track to the north-northwest and move into drier air, which will prevent further intensification.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…
Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Diego have deployed state-of-the art imaging techniques to discover the metabolism driving Alzheimer’s disease; results suggest new treatment strategies. Alzheimer’s disease causes significant problems with memory,…
A cause of immunodeficiency identified
After stroke and heart attack: Every year, between 250,000 and 300,000 people in Germany suffer from a stroke or heart attack. These patients suffer immune disturbances and are very frequently…





















