Modeling magma to find copper
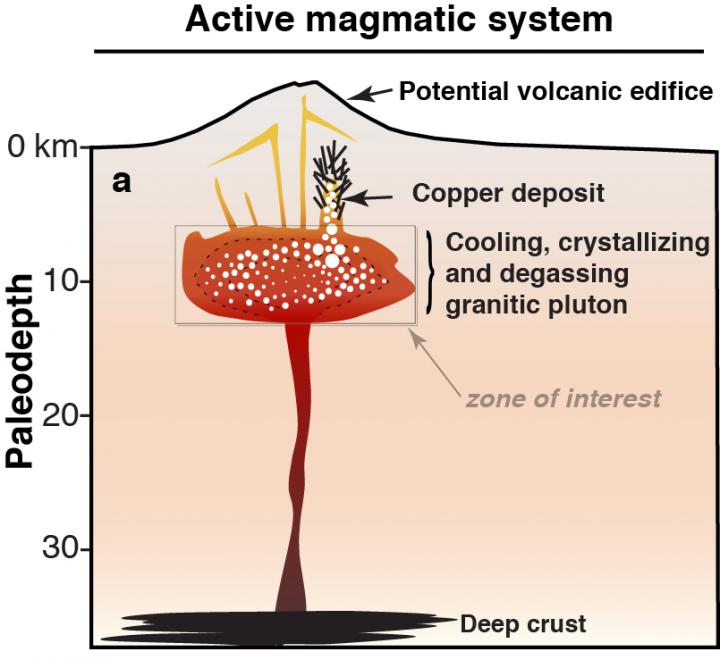
This is an activ magmatic system. Credit: ©UNIGE
Despite similar ore forming processes, the size of these deposits can vary orders of magnitude from one place to another, the main reason of which has remained unclear.
A new study led by researchers from the Universities of Geneva (UNIGE, Switzerland) and the Saint-Etienne (France), to be published in Scientific Reports, suggests that the answer may come from the volume of magma emplaced in the crust and proposes an innovative method to better explore these deposits.
Magmas formed above subduction zones contain important amount of water that is essentially degassed during volcanic eruptions or upon magma cooling and solidification at depth.
The water escaping from the crystallizing magma at several kilometers below surface carries most of the copper initially dissolved in the magma. On its way toward the surface the magmatic fluids cool and deposit copper in the fractured rocks forming giant metal deposits such as those exploited along the Andean Cordillera.
By modeling the process of magma degassing, the researchers could reproduce the chemistry of the fluids that form metal deposits.
“Comparing the model results with available data from known copper deposits, we could link the timescales of magma emplacement and degassing in the crust, the volume of magma, and the size of the deposit”, explains Luca Caricchi, researcher at the UNIGE.
The scientists also propose a new method to estimate the size of the deposits, based on high-precision geochronology, one of the specialties of the Department of Earth Sciences in UNIGE's Science Faculty.
This technique is a new add-in in the prospector toolbox with the possibility to identify deposits with the best potential, early in the long and costly process of mineral exploration.
It is anticipated that the computational approach developed in this study can also provide important insights on the role of magma degassing as a potential trigger for volcanic eruptions.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















