Global Climate Trend Since Nov. 16, 1978: +0.14 C Per Decade
UAH March 2013 Layer = LT Lower Troposphere
Global climate trend since Nov. 16, 1978: +0.14 C per decade
March temperatures (preliminary)
Global composite temp.: +0.17 C (about 0.31 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
Northern Hemisphere: +0.34 C (about 0.61 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
Southern Hemisphere: ±0.00 C (about 0.00 degrees Fahrenheit) at 30-year average for March.
Tropics: ±0.00 C (about 0.00 degrees Fahrenheit) at 30-year average for March.
February temperatures (revised):
Global Composite: +0.17 C above 30-year average
Northern Hemisphere: +0.32 C above 30-year average
Southern Hemisphere: +0.02 C above 30-year average
Tropics: -0.10 C below 30-year average
(All temperature anomalies are based on a 30-year average (1981-2010) for the month reported.)
Notes on data released April 7, 2014:
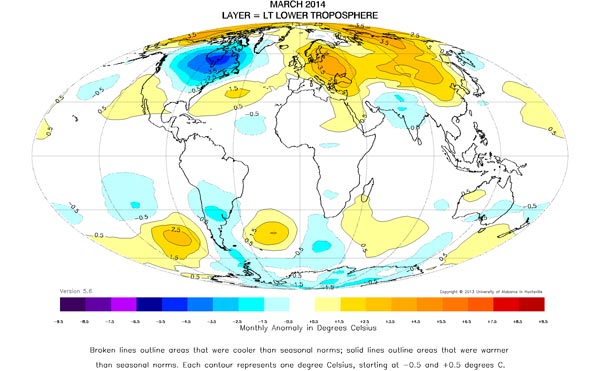
March was similar to February, in that warm and cold areas balanced each other in the tropics and Southern Hemisphere, according to Dr. John Christy, a professor of atmospheric science and director of the Earth System Science Center at The University of Alabama in Huntsville. North America was cooler than normal, while Eurasia was warmer. March was the sixth month in a row with below normal temperatures in the lower 48 states.
Compared to seasonal norms, the coldest place in Earth's atmosphere in March was over south central Hudson Bay, where temperatures were as much as 4.87 C (about 8.8 degrees Fahrenheit) cooler than seasonal norms. Compared to seasonal norms, the warmest departure from average in March was along Russia’s northernmost Arctic coast near Faddey Bay. Temperatures there were as much as 4.7 C (8.5 degrees Fahrenheit) warmer than seasonal norms.
Archived color maps of local temperature anomalies are available on-line at:
As part of an ongoing joint project between UAHuntsville, NOAA and NASA, Christy and Dr. Roy Spencer, an ESSC principal scientist, use data gathered by advanced microwave sounding units on NOAA and NASA satellites to get accurate temperature readings for almost all regions of the Earth. This includes remote desert, ocean and rain forest areas where reliable climate data are not otherwise available.
The satellite-based instruments measure the temperature of the atmosphere from the surface up to an altitude of about eight kilometers above sea level. Once the monthly temperature data is collected and processed, it is placed in a “public” computer file for immediate access by atmospheric scientists in the U.S. and abroad.
Neither Christy nor Spencer receives any research support or funding from oil, coal or industrial companies or organizations, or from any private or special interest groups. All of their climate research funding comes from federal and state grants or contracts.
Dr. John Christy, (256) 961-7763
john.christy@nsstc.uah.edu
Dr. Roy Spencer, (256) 961-7960
roy.spencer@nsstc.uah.edu
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















