Strongest Ever Spin-Phonon Coupling Observed
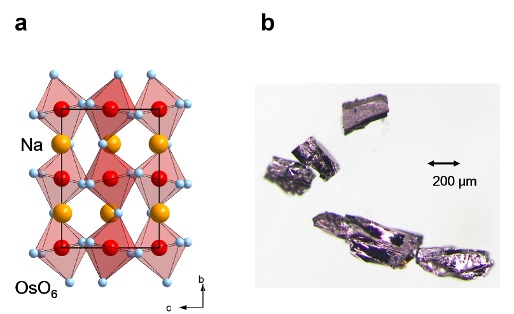
Figure: (a) Schematic of an osmium oxide (NaOsO3) crystal structure and (b) an optical microscope image of the single crystal. Copyright : National Institute for Materials Science
A research team led by Kazunari Yamaura, chief researcher, Superconducting Properties Unit, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), Japan, and Dr. Stuart Calder and others at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the United States, jointly demonstrated that the strongest ever spin-phonon coupling was observed in osmium oxide synthesized for the first time in the world by NIMS in 2009. A general belief is that the stronger the coupling between various properties in a material is, the more advantageous it is in the development of a new functional material. As such, the osmium oxide may serve as a candidate for a next-generation functional material useful in the areas of information & technology and electronics.
While platinum group elements and their compounds are widely used as catalysts, their other functions have not been explored very much, partly because they are expensive. Amid the situation, the NIMS research team discovered that the osmium oxide it synthesized in 2009 exhibits an unusual magnetic transition at about 140°C, which is higher than room temperature, and had been taking on the challenge of pioneering non-catalytic, industrial functions of the material.
Based on the recent observation of spin-phonon coupling in the osmium oxide, the team found that the coupling was the strongest ever observed. The strong spin-phonon coupling may be caused by the outermost orbitals of osmium atoms as they are greatly extended outward in space, in the solid oxide. The fact that this structural characteristic is common to all platinum group elements suggests that compounds based on these elements other than osmium are also likely to be associated with strong spin-phonon coupling.
Spin-phonon coupling directly represents the strength of interaction between magnetism (spin) and the crystal lattice system (phonon). Recent studies indicate that the stronger the spin-phonon interaction is, the more favorable it is in the development of new materials—such as a multiferroic material, for example—in which the coupling of magnetism and the lattice system has great importance. Expectations are rising for the multiferroic material as a candidate for an innovative functional material, as it may contribute to the realization of power-saving high-density information-recording elements and power-saving ultra-high-speed logic elements. This study is considered to be a major step toward this endeavor.
This research was carried out in the framework of the NIMS 3rd Mid-Term Program project on advanced superconducting materials.
(This study was published in Nature Communications on Nov. 26, 2015: S. Calder, J.H. Lee, M.B. Stone, M.D. Lumsden, J.C. Lang, M. Feygenson, Z. Zhao, J.-Q. Yan, Y.G. Shi, Y.S. Sun, Y. Tsujimoto, K. Yamaura, and A.D. Christianson: “Enhanced spin-phonon-electronic coupling in a 5d oxide”: doi:10.1038/ncomms9916)
Associated links
Original article from National Institute for Materials Science
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















