Physicists discover material for a more efficient energy storage
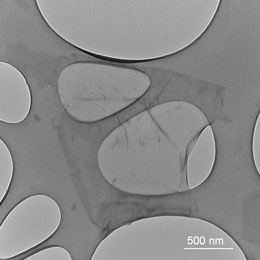
Graphene flakes in the graphene plastics compound University of Luxembourg
These calculations could now be confirmed by experiment in cooperation with the “Centre de Recherche Paul Pascal” in Bordeaux, France, and resulted in the discovery of a so-called high-k-material, which might enable the production of better energy storage devices – the basis for smaller, faster and more efficient electronics.
The earlier calculations made by the team around Tanja Schilling, professor of physics at the University of Luxembourg, were at first rather bad news for the field of materials research: they indicated that certain compound materials made of polymers and flaky graphene, unlike those made of polymers and carbon nanotubes, did not increase the conductivity of the material to the degree that was generally expected until then. It was a surprising conclusion at the time which questioned the use of graphene in order to increase conductivity.
This prediction, however, now lead to a highly promising discovery: the effect that put the conductivity of the plastics-graphene-compound into question, causes it to have remarkable dielectric properties. This means that one can generate a strong electric field inside of it – the fundamental property for the production of efficient capacitors.
These are tiny components that can store energy statically and occur in almost all electronic devices, where they act as voltage regulators or information storage, among other things. Computers, for example, contain billions of those.
“Materials with a high dielectric constant, so-called high-k-materials, are highly sought after,” says Tanja Schilling, head of the research project at the Faculty of Science, Technology and Communication of the University of Luxembourg. “The discovery based on our predictions was now published in the renowned journal Nature Communications – which we are very happy about.”
The special dielectric properties of the compound material occur as a result of its liquid crystal properties impeding the arrangement of the graphene flakes into a conducting structure. So when there is an electric current, it does not flow directly through the compound, but instead generates a strong electric field.
While in other compound materials the current permeable effect is the dominant one, the Luxembourg physicists could demonstrate mathematically that, in this case, the liquid crystal properties play the major role and are responsible for the unexpected electric properties.
The chemicals company Solvay, partner of the research project, now wants to continue the research around this new high-k-material, aiming to produce synthetics for particularly efficient capacitors and further applications in the future.
Notes to the editor:
The article “Graphene Liquid Crystal Retarded Percolation for New High-k Materials” is published in the scientific journal “Nature Communications” (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9700).
http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2015/151116/ncomms9700/full/ncomms9700.html?WT.ec_i… – Link to the scientific publication
http://www.uni.lu – homepage of the University of Luxembourg
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















