Physicist says nanoparticle assembly is like building with LEGOs
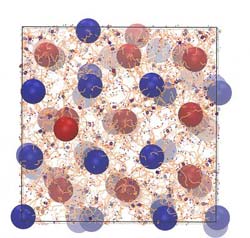
This image shows a crystal of nanoparticles (the red and blue spheres) held together by DNA strands (the orange lines) via the hybridization of complementary sequences (the blue and red rings). Credit: Image courtesy of Chris Knorowski/Iowa State University/Ames Laboratory<br>
Travesset, an associate professor of physics and astronomy and an associate of the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory, writes in the journal's Perspectives section that the controlled self-assembly of nanoparticles could help researchers create new materials with unique electrical, optical, mechanical or transport properties.
“Nanoparticle self-assembly has entered the LEGO era,” Travesset said. “You can really work with nanoparticles in the same way you can work with LEGOs. This represents a breakthrough in the way we can manipulate matter. Really revolutionary applications will come.”
In his commentary, Travesset reports on the ramifications of a scientific paper also published in the Oct. 14 issue of Science. Lead authors of the scientific paper are Chad Mirkin, director of the International Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and George Schatz, a professor of chemistry at Northwestern. Their research team describes new technologies that use complementary DNA strands to link nanoparticles and control how the particles precisely assemble into target structures.
Nanoparticles are so small – just billionths of a meter – that it is practically impossible to assemble real materials particle by particle. Past attempts to induce their self-assembly have been successful in only a handful of systems and in very restrictive conditions.
The developments by the Mirkin and Schatz research team are “likely to elevate DNA-programmed self-assembly into a technique for the design of nanoparticle structures a la carte,” Travesset wrote.
Travesset's research program includes theoretical studies of the assembly of nanoparticles and how they can be uniformly mixed with polymers. A research paper describing some of his findings was published in the May 27 issue of the journal Physical Review Letters (Dynamics and Statics of DNA-Programmable Nanoparticle Self-Assembly and Crystallization).
With the development of efficient self-assembly technologies, Travesset said there's tremendous potential for nanoparticle science.
“Being able to assemble nanoparticles with such control represents a major accomplishment in our quest to manipulate matter,” he wrote in Science. “There are immediate important applications related to catalysis, medical sensing, new optical materials or metamaterials, and others that will follow from these studies.
“Most likely, however, many other applications will arise as we dig deeper, understand better, expand further, and tinker with the opportunities provided by these materials.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ameslab.govAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















