Packing Electrons in a Nano Box: Control of Many-Body Correlation by Quantum Confinement
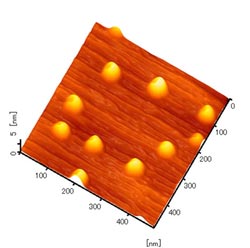
Atomic force microscope image of GaAs quantum dots used in this research.<br>
A team headed by Dr. Takashi Kuroda, Senior Researcher, and Dr. Marco Abbarchi, Researcher, of the Quantum Dot Research Center (Managing Director: Kazuaki Sakoda), National Institute for Materials Science (President: Sukekatsu Ushioda), in joint research with Hokkaido University, succeeded in controlling the few-particle quantum state of a semiconductor quantum dot, and changing its correlation energies. This research achievement will make it possible to develop semiconductor non-linear devices which enable stable drive with low power consumption.
When an electron and proton are brought into proximity in vacuum, the two particles are mutually attracted by Coulomb force and form a hydrogen atom. If another electron or proton is placed in addition, the many-body effect will result in formation of an ionic hydrogen molecule comprising a total of three particles.
This kind of quantum state also exists in solids. A pair of an electron and hole in a semiconductor form an exciton, analogous to a hydrogen atom. If another electron or hole is added, a complex state of three particles, called a charged exciton, is formed. In a semiconductor, unlike hydrogen in vacuum, it is possible to confine electrons an holes in quantum dots, i.e., an extremely small space on the order of several nanometers, and an increase in the stabilization energy of the multi-electronic state can be expected.
In this research, gallium arsenide (GaAs) quantum dots embedded in aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs), fabricated by the droplet epitaxy method were used. This method was originally developed by NIMS. As a distinctive feature of the quantum dots, the length of the crystal lattice is perfectly matched between the guest and host materials. As a result, an unprecedented clean quantum structure was realized. We succeeded in observation of charged excitons by measuring the photon emission signals from single quantum dots. In particular, when the stabilization energy of charged excitons was compared with that of a quantum well structure of the same type of material, which was previously known to be ~1 meV, it was found to have a value more than 10 times larger.
This increase in many-body energy is due to a remarkable increase in the Coulomb force between in the many-particle system resulting from packing electrons in a 3-dimensional nano-space. This result elucidates for the first time the effect of confinement of a multi-electron state in a nano-space, which had not been known in the past, and thus is a result with extremely large scientific impact. From the viewpoint of applied technology, because electron correlation is also the source of diverse types of non-linear effect devices such as optical switching devices and lasers, if interaction intensity can be controlled using nanostructures, this can be expected to lead to the development of optical semiconductor devices which enable stable drive with low power consumption.
This result was published in the American scientific journal, Physical Review B, Vol. 82, Issue 20, Page 201301(R) (Nov. 15, 2010, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.201301) under the title: Energy renormalization of exciton complexes in GaAs quantum dots, by M. Abbarchi et al.
For more information:
Takashi Kuroda
Nanophotonics Group, Quantum Dot Research Center
National Institute for Materials Science
TEL +81-29-860-4194
E-mail: kuroda.takashi@nims.go.jp
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















