Manchester scientists tie the tightest knot ever achieved
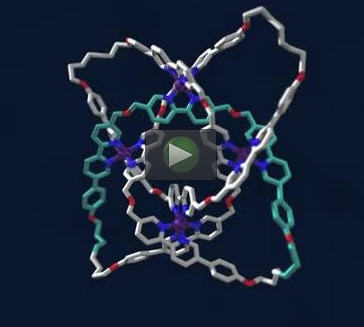
The X-ray crystal structure of a 192-atom-loop molecular 819 knot featuring iron ions (shown in purple), oxygen atoms (red), nitrogen atoms (dark blue), carbon atoms (shown in metallic grey, with one of the building blocks shown in light blue) and a single chloride ion (green) at the center of the structure. Credit: Robert W. McGregor (www.mcgregorfineart.com).
The University of Manchester researchers, led by Professor David Leigh in Manchester's School of Chemistry, have developed a way of braiding multiple molecular strands enabling tighter and more complex knots to be made than has previously been possible.
The breakthrough knot has eight crossings in a 192-atom closed loop – which is about 20 nanometres long (ie 20 millionths of a millimeter).
Being able to make different types of molecular knots means that scientists should be able to probe how knotting affects strength and elasticity of materials which will enable them to weave polymer strands to generate new types of materials.
Professor David Leigh said: “Tying knots is a similar process to weaving so the techniques being developed to tie knots in molecules should also be applicable to the weaving of molecular strands.
“For example, bullet-proof vests and body armour are made of kevlar, a plastic that consists of rigid molecular rods aligned in a parallel structure – however, interweaving polymer strands have the potential to create much tougher, lighter and more flexible materials in the same way that weaving threads does in our everyday world.
“Some polymers, such as spider silk, can be twice as strong as steel so braiding polymer strands may lead to new generations of light, super-strong and flexible materials for fabrication and construction.”
Professor David Leigh said he and his team were delighted to have achieved this scientific landmark.
He explained the process behind their success: “We 'tied' the molecular knot using a technique called 'self-assembly', in which molecular strands are woven around metal ions, forming crossing points in the right places just like in knitting – and the ends of the strands were then fused together by a chemical catalyst to close the loop and form the complete knot.
“The eight-crossings molecular knot is the most complex regular woven molecule yet made by scientists.”
The research breakthrough will be published in the prestigious journal Science on 13 January 2017 in a paper entitled: 'Braiding a molecular knot with eight crossings'
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















