A new form of carbon: Grossly warped 'nanographene'
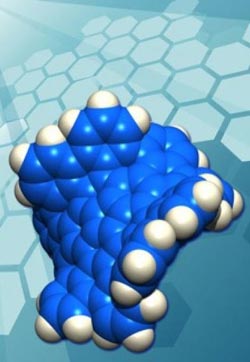
Chemists at Boston College and Nagoya University in Japan have synthesized the first example of a new form of carbon. The new material consists of multiple identical pieces of "grossly warped graphene," each containing exactly 80 carbon atoms joined together in a network of 26 rings, with 30 hydrogen atoms decorating the rim. Because they measure slightly more than a nanometer across, these individual molecules are referred to generically as "nanocarbons."<br><br>Credit: Nature Chemistry<br>
Chemists at Boston College and Nagoya University in Japan have synthesized the first example of a new form of carbon, the team reports in the most recent online edition of the journal Nature Chemistry.
The new material consists of multiple identical pieces of grossly warped graphene, each containing exactly 80 carbon atoms joined together in a network of 26 rings, with 30 hydrogen atoms decorating the rim. Because they measure slightly more than a nanometer across, these individual molecules are referred to generically as “nanocarbons,” or more specifically in this case as “grossly warped nanographenes.”
Until recently, scientists had identified only two forms of pure carbon: diamond and graphite. Then in 1985, chemists were stunned by the discovery that carbon atoms could also join together to form hollow balls, known as fullerenes. Since then, scientists have also learned how to make long, ultra-thin, hollow tubes of carbon atoms, known as carbon nanotubes, and large flat single sheets of carbon atoms, known as graphene. The discovery of fullerenes was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1996, and the preparation of graphene was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010.
Graphene sheets prefer planar, 2-dimensional geometries as a consequence of the hexagonal, chicken wire-like, arrangements of trigonal carbon atoms comprising their two-dimensional networks. The new form of carbon just reported in Nature Chemistry, however, is wildly distorted from planarity as a consequence of the presence of five 7-membered rings and one 5-membered ring embedded in the hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms.
Odd-membered-ring defects such as these not only distort the sheets of atoms away from planarity, they also alter the physical, optical, and electronic properties of the material, according to one of the principle authors, Lawrence T. Scott, the Jim and Louise Vanderslice and Family Professor of Chemistry at Boston College.
“Our new grossly warped nanographene is dramatically more soluble than a planar nanographene of comparable size,” said Scott, “and the two differ significantly in color, as well. Electrochemical measurements revealed that the planar and the warped nanographenes are equally easily oxidized, but the warped nanographene is more difficult to reduce.”
Graphene has been highly touted as a revolutionary material for nanoscale electronics. By introducing multiple odd-membered ring defects into the graphene lattice, Scott and his collaborators have experimentally demonstrated that the electronic properties of graphene can be modified in a predictable manner through precisely controlled chemical synthesis.
The leader of the team in Japan, Professor Kenichiro Itami, is Director of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules at the University of Nagoya. The other authors of this paper include Dr. Yasutomo Segawa, an assistant professor at the University of Nagoya, Dr. Qianyan Zhang, a post-doctoral researcher at Boston College, and Katsuaki Kawasumi, a Ph.D. student from Nagoya who worked for three months during the course of this project as a visiting student at Boston College with a fellowship from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.bc.eduAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…