X-ray scattering shines light on protein folding
The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state. Credit: Professor Hyotcherl Ihee, KAIST Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee's group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
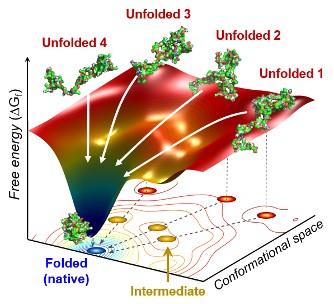
Ihee's team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don't know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein's folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
###
Ihee's group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















