SKINSPECTION – Hybrid Imaging for Skin Diagnosis

The incidence of skin cancer in Europe, US and Australia is rising rapidly. One in five will develop some form of skin cancer during the lifetime. A person has a 1:33 chance to develop melanoma, the most aggressive skin cancer.
Melanoma is the second most common cancer in women aged 20-29, and the sixth most common cancer in men and women. In 2007, more than 1 million new cases were diagnosed in the US alone.
About 90% of skin cancers are caused by ultraviolet (UV) sunlight. A significant improvement of the current diagnostic tools of dermatologists is required in order to identify dermal disorders at a very early stage as well as to monitor directly the effects of treatment.
In the context of the SKINSPECTION project, a European consortium has developed a novel multimodal hybrid diagnostic imaging system with the capability to perform non-invasive high resolution three-dimensional imaging in-vivo.
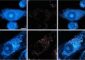
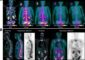
The SKINSPECTION approach combines two-photon imaging with time-correlated single photon detection, autofluorescence lifetime imaging, high-frequency ultrasound and optoacoustic imaging. The innovative combination of these modalities allows to obtain a wide-field view with quantitative depth information of skin lesions and a close-look into particular intra-tissue compartments with quantitative hyperspectral information and subcellular resolution. The goal of the project is to provide a novel unique tool for early diagnosis and treatment control of skin cancer and skin disease.
For achieving this objective, two systems for microscopic and macroscopic imaging of lesions were developed in the last 3 years by the partners JenLab GmbH and Imperial College London (two-photon microscopy/FLIM) and Fraunhofer IBMT (Fraunhofer Institute for Biomedical Engineering) and kibero GmbH (optoacoustic/ultrasound imaging). The systems were successfully certified for clinical studies and are currently being evaluated for imaging of skin lesions in a bicentric clinical trial at Hammersmith Hospital and Universita di Modena.
Contact:
Dr. Marc Fournelle
Biomedical Ultrasound Research
Fraunhofer IBMT
Tel: +49 6894 / 980-220
Fax: +49 6894 / 980-234
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…