Rogue enzymes cause numerous diseases
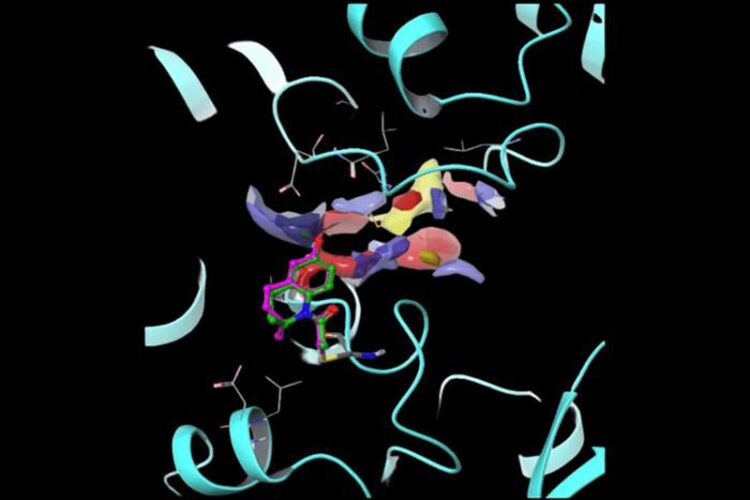
Computational docking model of covalent inhibitors bound to the SARS-CoV-2 helicase.
Credit: Lawrence Ruben Laboratory of Chemistry and Cell Biology at The Rockefeller University
A new method could help design drugs to treat them.
Helicases are enzymes that unwind DNA and RNA. They’re central to cellular life, implicated in a number of cancers and infections—and, alas, extraordinarily difficult to target with drugs.
Now, new research provides a powerful platform for designing covalent inhibitors tailored to target helicases. The paper, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, describes how researchers used this innovative new platform to design molecules that take aim at helicases involved in COVID and certain cancers.
“High-resolution structural and biochemical data alone are not sufficient for finding druggable sites in conformationaly dynamic enzymes such as helicases,” says Rockefeller’s Tarun Kapoor. “Our approach can identify these sites and also provide chemical starting points for developing drugs that target helicases.”
Mechanical difficulties
Complex molecular machines that traverse DNA and RNA strands, helicases must kickstart the unraveling process that prepares genetic information for processes such as replication or transcription. But when helicases go rogue, they can promote the growth of some cancers. At the same time, helicases are also crucial for viral replication and bacterial proliferation. It follows that different drugs targeting these enzymes could treat certain cancers, or stop infections in their tracks.
“Helicases are very hot targets right now,” says lead author Jared Ramsey, a graduate student in the Kapoor lab. “Drugs that inhibit helicases are of great interest to the scientific community, and could be leveraged as new and effective treatments.”
Helicase inhibitors, however, are hard to come by. By testing thousands of small molecules, drug companies have occasionally happened upon methods for grinding one helicase or another to a halt, but these occurences have proven rare. “The same was true in our lab,” Ramsey says. “We were unable to identifiy helicase inhibitors using typical approaches such as high-throughput screening.”
Ramsey, Kapoor, and colleagues wondered whether electrophilic small molecules could be used to scout out the weak points in a helicase, quietly prodding the enzyme for potential binding sites susceptible to drugs. Central to this idea is the concept of covalency, where inhibitor candidates irreversibly bind the helicase target, possibly circumventing complications from the dynamic and fluid nature of these enzymes. To that end, the team selected two innocuous molecules and directed the so-called scout fragments toward a helicase of SARS-CoV-2.
Once they found likely binding sites on the helicase, they promoted the scouts to soldiers. “We just had to take a minimally elaborated electrophilic molecule, identify where it binds with mass spectrometry, and then use medicinal chemistry to modify it and screen a few versions of to achieve a potent, specific inhibitor,” Ramsey says.
The team also demonstrated that scout fragments could be tuned to shut down two specific helicases, BLM and WRN, which are implicated in Bloom Syndrome and Werner Syndrome, respectively, as well as a number of cancers. While the published findings aren’t expected to immediately translate into drugs that treat COVID or cancer, they do serve as a valuable starting point for drug developers to make bespoke helicase targets.
“Our findings show how the platform we developed could accelerate work in other labs,” Ramsey says. “We take a basic science approach, and that’s how many useful findings are uncovered. This takes a challenging problem and gives us a solid place to start.”
Journal: JACS
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c10581
Media Contact
Katherine Fenz
Rockefeller University
kfenz@rockefeller.edu
Office: 212-327-7913
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















