Interstellar winds buffeting our solar system have shifted direction
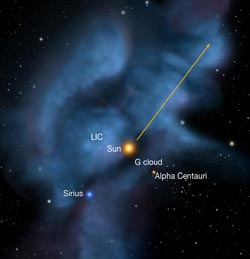
This image shows the nearest interstellar gas clouds around the solar system, including the Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC) and G Cloud, along with positions of neighboring stars in the plane of our Milky Way galaxy. The arrow shows the sun's motion relative to neighboring stars. Image courtesy of P.C. Frisch, University of Chicago <br>
The finding helps scientists map our location within the Milky Way galaxy and is crucial for understanding our place in the cosmos through the vast sweep of time—where we've come from, where we're currently located, and where we're going in our journey through the galaxy.
Additionally, scientists now gain deeper insight into the dynamic nature of the interstellar winds, which has major implications on the size, structure, and nature of our sun's heliosphere—the gigantic bubble that surrounds our solar system and helps shield us from dangerous incoming galactic radiation.
The results, based on data spanning four decades from 11 different spacecraft, including IBEX, were published in the journal Science September 5, 2013.
“It was very surprising to find that changes in the interstellar flow show up on such short time scales because interstellar clouds are astronomically large,” says Eberhard Möbius, UNH principal scientist for the IBEX mission and co-author on the Science paper. Adds Möbius, “However, this finding may teach us about the dynamics at the edges of these clouds—while clouds in the sky may drift along slowly, the edges often are quite fuzzy and dynamic. What we see could be the expression of such behavior.”
The data from the IBEX spacecraft show that neutral interstellar atoms are flowing into the solar system from a different direction than previously observed. Interstellar atoms flow past the Earth as the interstellar cloud surrounding the solar system passes the sun at 23 kilometers per second (50,000 miles per hour).
The latest IBEX measurements of the interstellar wind direction differed from those made by the Ulysses spacecraft in the 1990s. That difference led the IBEX team to compare the IBEX measurements to data gathered by 11 spacecraft between 1972 and 2011. The scientists wanted to gather as much evidence from as many sources as possible to determine whether the newer instruments simply provided more accurate results, or whether the wind direction itself changed over the years.
The various sets of observations relied on three different methods to measure the incoming interstellar wind. IBEX and Ulysses directly measured neutral helium atoms as they coursed through the inner solar system. IBEX's measurements are close to Earth, while Ulysses' measurements were taken between 1.3 and 2 times further from the sun.
In the final analysis, the direction of the wind obtained most recently by IBEX data differs from the direction obtained from the earlier measurements, which strongly suggests the wind itself has changed over time.
“Prior to this study, we were struggling to understand why our current measurements from IBEX differed from those of the past,” says co-author Nathan Schwadron, lead scientist for the IBEX Science Operations Center at UNH. “We are finally able to resolve why these fundamental measurements have been changing with time: we are moving through a changing interstellar medium.”
The paper, “Decades-long Changes of the Interstellar Wind Through our Solar System,” includes IBEX team members from the University of Chicago, the Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the Southwest Research Institute, the University of Texas in San Antonio, UNH, Dartmouth College, Central Arizona College, the University of California at Berkeley, and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
IBEX is part of NASA's series of low-cost, rapidly developed Small Explorer space missions. Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio leads the IBEX mission with teams of national and international partners. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., manages the Explorers Program for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
The University of New Hampshire, founded in 1866, is a world-class public research university with the feel of a New England liberal arts college. A land, sea, and space-grant university, UNH is the state's flagship public institution, enrolling 12,200 undergraduate and 2,300 graduate students.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unh.eduAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















