Cavitation aggressive intensity greatly enhanced using pressure at bubble collapse region
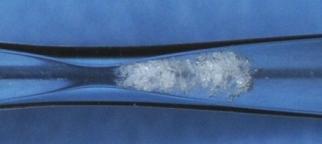
This image shows hydrodynamic cavitation through a venturi tube. Credit: Hitoshi Soyama
Cavitation – the formation, growth and subsequent collapse of microbubbles – produces high, localized energy which can be used in chemical processes for treating water and the pretreatment of biomass.
The research team found that the conventional cavitation method of applying ultrasonic energy was not strong enough, so they proposed using hydrodynamic cavitation instead.
In the proposed method, test water is passed through a constriction tube. Hydrodynamic cavitation is then produced by the decrease of pressure due to the increase of flow velocity.
The team found that the aggressive intensity of hydrodynamic cavitation was optimized with an increase of pressure at the bubble collapse region.
Although most researchers believe that an enlarged cavitation area produces aggressive intensity, by contrast, it seems a rise in aggressive intensity can occur with a reduced cavitation area. In the research experiments, the size of the cavitating region was reduced by varying the upstream and downstream pressures.
The team has demonstrated the enhancement of cavitation aggressive intensity by a factor of about 100 by optimizing pressure at the region, measuring acoustic power at cavitation bubble collapse, and luminescence as a function of the pressure.
This method can be useful for practical applications, as it does not need additional power, but the aggressive intensity can be increased simply by controlling a valve downstream to the cavitating region.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















